 Piri Re'is[1] states that Colombo was Genoese.
Piri Re'is[1] states that Colombo was Genoese.Mavi Boncuk |
Translated off the map Also note them being discovered before he ever arrived
These coasts are named the shores of Antilia. They were discovered in the year 896 of the Arab calendar. But it is reported thus, that a Genoese infidel, his name was Colombo, be it was who discovered these places. For instance, a book fell into the hands of the said Colombo, and be found it said in this book that at the end of the Western Sea [Atlantic] that is, on its western side, there were coasts and islands and all kinds of metals and also precious stones. The above-mentioned, having studied this book thoroughly, explained these matters one by one to the great of Genoa and said: "Come, give me two ships, let me go and find these places." They said: "O unprofitable man, can an end or a limit be found to the Western Sea? Its vapour is full of darkness." The above-mentioned Colombo saw that no help was forthcoming from the Genoese, he sped forth, went to the Bey of Spain [king], and told his tale in detail. They too answered like the Genoese. In brief Colombo petitioned these people for a long time, finally the Bey of Spain gave him two ships, saw that they were well equipped, and said:
"O Colombo, if it happens as you say, let us make you kapudan [admiral] to that country." Having said which he sent the said Colombo to the Western Sea. The late Gazi Kemal had a Spanish slave. The above-mentioned slave said to Kemal Reis, he had been three times to that land with Colombo. He said: "First we reached the Strait of Gibraltar, then from there straight south and west between the two . . . [illegible]. Having advanced straight four thousand miles, we saw an island facing us, but gradually the waves of the sea became foamless, that is, the sea was becalmed and the North Star--the seamen on their compasses still say star--little by little was veiled and became invisible, and be also said that the stars in that region are not arranged as here. They are seen in a different arrangement. They anchored at the island which they had seen earlier across the way, the population of the island came, shot arrows at them and did not allow them to land and ask for information. The males and the females shot hand arrows. The tips of these arrows were made of fishbones, and the whole population went naked and also very . . . [illegible]. Seeing that they could not land on that island; they crossed to the other side of the island, they saw a boat. On seeing them; the boat fled and they [the people in the boat] dashed out on land. They [the Spaniards] took the boat. They saw that inside of it there was human flesh. It happened that these people were of that nation which went from island to island hunting men and eating them. They said Colombo saw yet another island, they neared it, they saw that on that island there were great snakes. They avoided landing on this island and remained there seventeen days. The people of this island saw that no harm came to them from this boat, they caught fish and brought it to them in their small ship's boat [filika]. These [Spaniards] were pleased and gave them glass beads. It appears that he [Columbus] had read-in the book that in that region glass beads were valued. Seeing the beads they brought still more fish. These [Spaniards] always gave them glass beads. One day they saw gold around the arm of a woman, they took the gold and gave her beads. They said to them, to bring more gold, we will give you more beads, [they said]. They went and brought them much gold. It appears that in their mountains there were gold mines. One day, also, they saw pearls in the hands of one person. They saw that when; they gave beads, many more pearls were brought to them. Pearls were found on the shore of this island, in a spot one or two fathoms deep. And also loading their ship with many logwood trees and taking two natives along, they carried them within that year to the Bey of Spain. But the said Colombo, not knowing the language of these people, they traded by signs, and after this trip the Bey of Spain sent priests and barley, taught the natives how to sow and reap and converted them to his own religion. They had no religion of any sort. They walked naked and lay there like animals. Now these regions have been opened to all and have become famous. The names which mark the places on the said islands and coasts were given by Colombo, that these places may be known by them. And also Colombo was a great astronomer. The coasts and island on this map are taken from Colombo's map."
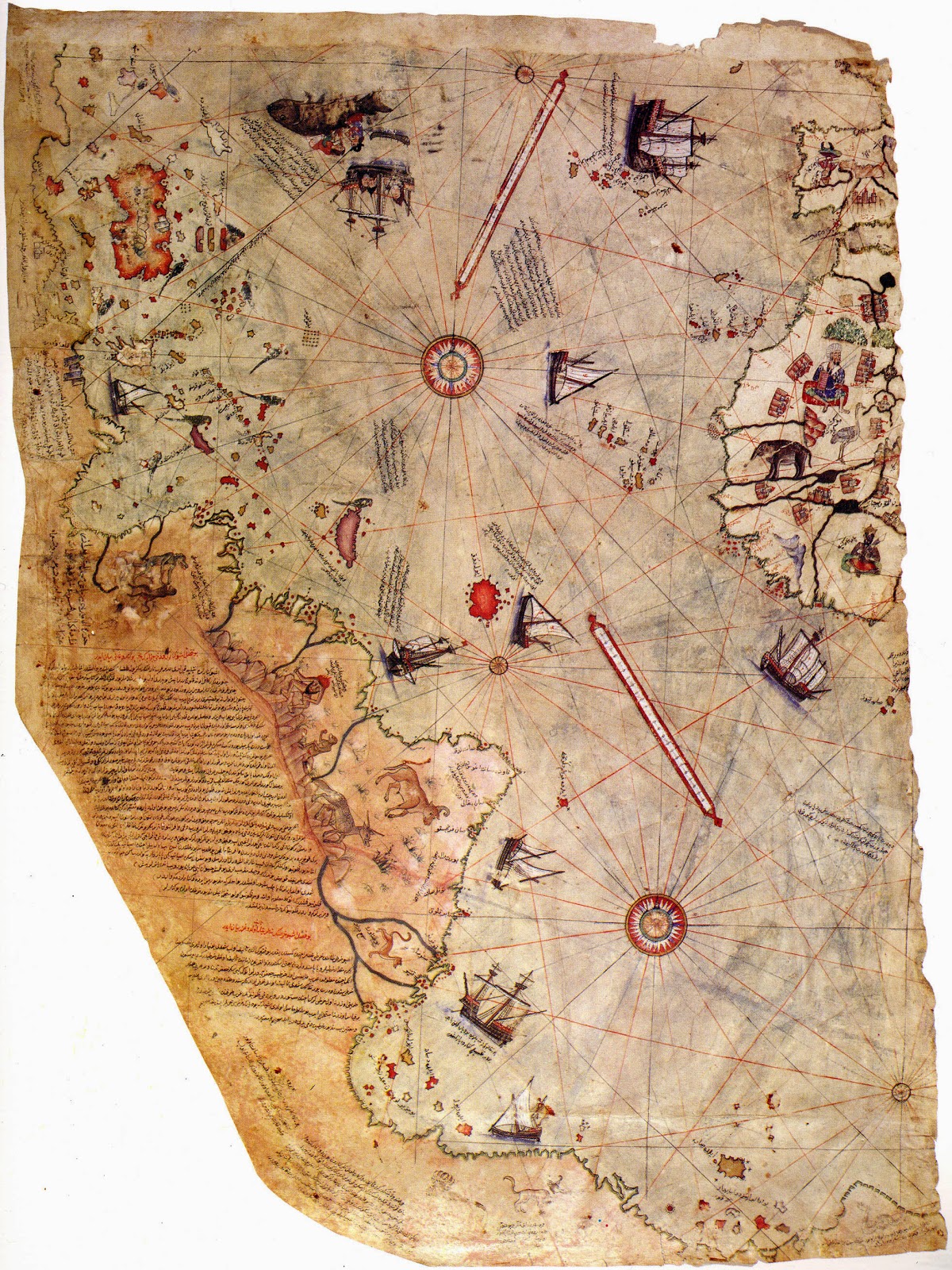
 Pictured: Surviving fragment of the second World Map of Piri Reis (1528)
Pictured: Surviving fragment of the second World Map of Piri Reis (1528) [1] Piri Reis (Turkish: Pîrî Reis or Muhyiddin Pîrî Bey also known as Hacı Ahmed Muhiddin Piri; "Reis" being a military rank) was an Ottoman admiral, geographer, and cartographer born between 1465 and 1470. He was executed in 1553.
He is primarily known today for his maps and charts collected in his Kitab-ı Bahriye (Book of Navigation), a book that contains detailed information on navigation, as well as very accurate charts (for their time) describing the important ports and cities of the Mediterranean Sea. He gained fame as a cartographer when a small part of his first world map (prepared in 1513) was discovered in 1929 at the Topkapı Palace in Istanbul. His world map is the oldest known Turkish atlas showing the New World, and one of the oldest maps of America still in existence anywhere (the oldest known map of America that is still in existence is the map drawn by Juan de la Cosa in 1500). Piri Reis' map is centered on the Sahara at the latitude of the Tropic of Cancer.
In 1528, Piri Reis drew a second world map, of which a small fragment (showing Greenland and North America from Labrador and Newfoundland in the north to Florida, Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica and parts of Central America in the south) still survives. According to his imprinting text, he had drawn his maps using about 20 foreign charts and mappae mundi (Arab, Spanish, Portuguese, Chinese, Indian and Greek) including one by Christopher Columbus.